All About the Betel Nut Palm: A Comprehensive Guide

Chính Sách Vận Chuyển Và Đổi Trả Hàng
Miễn phí vận chuyển mọi đơn hàng từ 500K
- Phí ship mặc trong nước 50K
- Thời gian nhận hàng 2-3 ngày trong tuần
- Giao hàng hỏa tốc trong 24h
- Hoàn trả hàng trong 30 ngày nếu không hài lòng
Mô tả sản phẩm
What is the Betel Nut Palm?
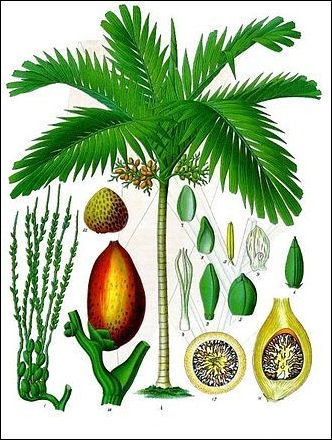
The betel nut palm, scientifically known as Areca catechu, is a tropical tree native to Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands. This slender, evergreen palm is renowned for its seeds, commonly called betel nuts, which are chewed for their stimulant effects. The tree typically grows up to 20 meters tall, featuring a smooth, ringed trunk and pinnate leaves that can reach 1-2 meters in length. Its fruit, the betel nut, is enclosed in a fibrous husk and turns yellow-orange when ripe. Evidence from archaeological findings in the Philippines and Vietnam suggests that betel nut chewing dates back at least 4,000 years, highlighting its deep cultural roots in the region.How is the Betel Nut Palm Cultivated?
Cultivating the betel nut palm requires specific tropical conditions, including high humidity, temperatures between 20-40°C, and well-drained soil. Farmers typically propagate the tree through seeds, which germinate within 6-8 weeks. Young palms are transplanted to fields after 6-12 months, spaced 2-3 meters apart to allow growth. According to a 2020 FAO report, India is the world's largest producer of betel nuts, followed by Bangladesh and Indonesia. The trees begin bearing fruit after 5-7 years and can remain productive for 50-60 years, with annual yields ranging from 500-1,000 nuts per tree. Irrigation and organic fertilizers significantly boost production, as demonstrated by a 2018 study from the University of Agricultural Sciences, Bengaluru.What are the Traditional Uses of Betel Nut?
Betel nut holds immense cultural and ceremonial significance across Asia. In countries like India, Myanmar, and Papua New Guinea, it's traditionally offered to guests as a sign of respect and served at weddings and religious ceremonies. The nut is often chewed wrapped in betel leaves (Piper betle) with slaked lime, creating a stimulant mixture called "paan." The World Health Organization notes that approximately 600 million people worldwide practice betel nut chewing. Ayurvedic medicine has used betel nut for centuries to treat digestive issues, parasitic infections, and as an aphrodisiac, though modern research cautions against excessive use due to health risks.What are the Health Effects of Betel Nut Consumption?
Betel nut consumption has complex health implications that researchers continue to study. The nut contains arecoline, an alkaloid that stimulates the central nervous system, increasing alertness similar to caffeine. However, long-term use is strongly associated with oral submucous fibrosis, a precancerous condition, and oral cancer. A 2019 meta-analysis in The Lancet Oncology found that regular betel nut chewers have a 7-8 times higher risk of oral cancer than non-users. The International Agency for Research on Cancer classifies betel nut as a Group 1 carcinogen. Conversely, controlled traditional medicinal uses show potential benefits - a 2017 study in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology reported antimicrobial properties against certain pathogens.How Does the Betel Nut Palm Impact Local Economies?
The betel nut palm plays a vital economic role in producing regions. In India's Karnataka state alone, betel nut cultivation supports over 500,000 farming families, generating approximately $1.2 billion annually according to 2021 state agriculture department data. The global betel nut market was valued at $1.04 billion in 2022, projected to grow at 4.3% CAGR through 2030 (Grand View Research). However, economic benefits come with challenges - price volatility often leaves farmers vulnerable, as seen during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic when prices dropped 40% in Indonesia due to reduced ceremonial demand. Sustainable farming initiatives and value-added products (like betel nut-based medicines) are emerging as solutions to stabilize incomes.What is the Ecological Importance of Betel Nut Palms?
Betel nut palms contribute significantly to tropical ecosystems. Their extensive root systems help prevent soil erosion, particularly in monsoon-prone regions like coastal Bangladesh. A 2021 study in the Journal of Tropical Agriculture found that betel nut plantations host 23% more bird species than monoculture palm oil farms. The trees also sequester carbon effectively - mature palms absorb approximately 12-15 kg CO2 annually. However, concerns exist about water usage; a single hectare of betel nut palms requires about 7 million liters of water yearly, which can strain resources in drought-prone areas as noted in a 2022 WWF report on Indonesian agriculture.Conclusion: Balancing Tradition and Modern Understanding
The betel nut palm represents a fascinating intersection of culture, economy, and ecology. While its seeds carry significant cultural heritage across Asia, modern science reveals both potential benefits and serious health risks associated with consumption. Economically, it supports millions of farmers but faces sustainability challenges. Ecologically, the palms offer environmental benefits but require careful water management. Moving forward, research into safer consumption methods, sustainable farming practices, and medicinal applications could help preserve the betel nut palm's cultural importance while mitigating its risks. As global awareness grows, this remarkable tree continues to spark important discussions about balancing tradition with contemporary health and environmental knowledge.Xem thêm: cây đậu muồng